* Migrating parsingcompetition to new API. * Removing ParsedJson |
||
|---|---|---|
| .circleci | ||
| .github/workflows | ||
| benchmark | ||
| dependencies | ||
| doc | ||
| extra | ||
| fuzz | ||
| images | ||
| include | ||
| jsonchecker | ||
| jsonexamples | ||
| scripts | ||
| singleheader | ||
| src | ||
| style | ||
| tests | ||
| tools | ||
| windows | ||
| .appveyor.yml | ||
| .clang-format | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .drone.yml | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| AUTHORS | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTORS | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| amalgamation.sh | ||
README.md
simdjson : Parsing gigabytes of JSON per second
 JSON is everywhere on the Internet. Servers spend a *lot* of time parsing it. We need a fresh approach. simdjson uses commonly available SIMD instructions and microparallel algorithms to parse JSON 2.5x faster than anything else out there.
JSON is everywhere on the Internet. Servers spend a *lot* of time parsing it. We need a fresh approach. simdjson uses commonly available SIMD instructions and microparallel algorithms to parse JSON 2.5x faster than anything else out there.
- Ludicrous Speed: Over 2.5x faster than other production-grade JSON parsers.
- Delightfully Easy: First-class, easy to use API.
- Complete Validation: Full JSON and UTF-8 validation, with no compromises.
- Rock-Solid Reliability: From memory allocation to error handling, simdjson's design avoids surprises.
This library is part of the Awesome Modern C++ list.
Quick Start
simdjson is easily consumable with a single .h and .cpp file.
-
Prerequisites:
g++orclang++. -
Pull simdjson.h and simdjson.cpp into a directory, along with the sample file twitter.json.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/simdjson/simdjson/master/singleheader/simdjson.h https://raw.githubusercontent.com/simdjson/simdjson/master/singleheader/simdjson.cpp https://raw.githubusercontent.com/simdjson/simdjson/master/jsonexamples/twitter.json -
Create
parser.cpp:#include "simdjson.h" int main(void) { simdjson::document::parser parser; simdjson::document& tweets = parser.load("twitter.json"); std::cout << tweets["search_metadata"]["count"] << " results." << std::endl; } -
c++ -o parser parser.cpp simdjson.cpp -std=c++17 -
./parser100 results.
Real-world usage
If you are planning to use simdjson in a product, please work from one of our releases.
Research article (VLDB Journal)
A description of the design and implementation of simdjson is in our research article:
- Geoff Langdale, Daniel Lemire, Parsing Gigabytes of JSON per Second, VLDB Journal 28 (6), 2019appear)
We also have an informal blog post providing some background and context.
Some people enjoy reading our paper:
Talks
QCon San Francisco 2019 (best voted talk):
Performance results
simdjson uses three-quarters less instructions than state-of-the-art parser RapidJSON and fifty percent less than sajson. To our knowledge, simdjson is the first fully-validating JSON parser to run at gigabytes per second on commodity processors.
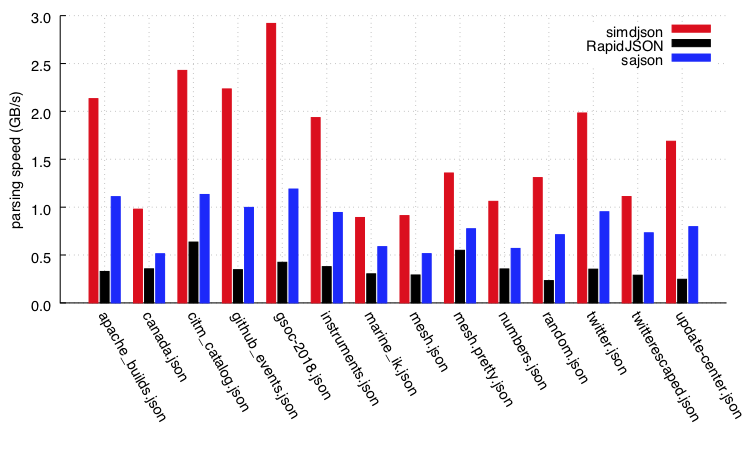
On a Skylake processor, the parsing speeds (in GB/s) of various processors on the twitter.json file are as follows.
| parser | GB/s |
|---|---|
| simdjson | 2.2 |
| RapidJSON encoding-validation | 0.51 |
| RapidJSON encoding-validation, insitu | 0.71 |
| sajson (insitu, dynamic) | 0.70 |
| sajson (insitu, static) | 0.97 |
| dropbox | 0.14 |
| fastjson | 0.26 |
| gason | 0.85 |
| ultrajson | 0.42 |
| jsmn | 0.28 |
| cJSON | 0.34 |
| JSON for Modern C++ (nlohmann/json) | 0.10 |
Requirements
- We support 64-bit platforms like Linux or macOS, as well as Windows through Visual Studio 2017 or later.
- A processor with
- AVX2 (i.e., Intel processors starting with the Haswell microarchitecture released 2013 and AMD processors starting with the Zen microarchitecture released 2017),
- or SSE 4.2 and CLMUL (i.e., Intel processors going back to Westmere released in 2010 or AMD processors starting with the Jaguar used in the PS4 and XBox One),
- or a any other x64 processor (going back to AMD Opteron in 2003 and the Pentium4 Prescott in 2004),
- or a 64-bit ARM processor (ARMv8-A): this covers a wide range of mobile processors, including all Apple processors currently available for sale, going as far back as the iPhone 5s (2013).
- A recent C++ compiler (e.g., GNU GCC or LLVM CLANG or Visual Studio 2017), we assume C++17. GNU GCC 7 or better or LLVM's clang 6 or better.
- Some benchmark scripts assume bash and other common utilities, but they are optional.
License
This code is made available under the Apache License 2.0.
Under Windows, we build some tools using the windows/dirent_portable.h file (which is outside our library code): it under the liberal (business-friendly) MIT license.
Runtime dispatch
On Intel and AMD processors, we get best performance by using the hardware support for AVX2 instructions. However, simdjson also runs on older Intel and AMD processors. The code automatically detects the feature set of your processor and switches to the right function at runtime (a technique sometimes called runtime dispatch).
On x64 hardware, you should typically build your code by specifying the oldest/less-featureful system you want to support so that runtime dispatch may work. If you build your code by asking the compiler to use more advanced instructions (e.g., -mavx2, /AVX2 or -march=haswell), then it may break runtime dispatch and your binaries will fail to run on older processors.
We also support 64-bit ARM (ARMv8-A). There is no runtime dispatch necessary on ARM.
You can check which CPU is being detected as follows:
simdjson::active_implementation->name(); // returns a descriptive string
Computed GOTOs
For best performance, we use a technique called "computed goto" when the compiler supports it, it is also sometimes described as "Labels as Values".
Though it is not part of the C++ standard, it is supported by many major compilers and it brings measurable performance benefits that
are difficult to achieve otherwise.
The computed gotos are automatically disabled under Visual Studio.
If you wish to forcefully disable computed gotos, you can do so by compiling the code with the macro SIMDJSON_NO_COMPUTED_GOTO
defined. It is not recommended to disable computed gotos if your compiler supports it. In fact, you should almost never need to
be concerned with computed gotos.
Thread safety
The simdjson library is mostly single-threaded. Thread safety is the responsibility of the caller: it is unsafe to reuse a document::parser object between different threads.
If you are on an x64 processor, the runtime dispatching assigns the right code path the first time that parsing is attempted. The runtime dispatching is thread-safe.
The json stream parser is threaded, using exactly two threads.
Large files
If you are processing large files (e.g., 100 MB), it is possible that the performance of simdjson will be limited by page misses and/or page allocation. On some systems, memory allocation runs far slower than we can parse (e.g., 1.4GB/s).
A viable strategy is to amortize the cost of page allocation by reusing the same parser object over several files:
// create one parser
simdjson::document::parser parser;
...
// the parser is going to pay a memory allocation price
auto [doc1, error1] = parser.parse(largestring1);
...
// use again the same parser, it will be faster
auto [doc2, error2] = parser.parse(largestring2);
...
auto [doc3, error3] = parser.load("largefilename");
If you cannot reuse the same parser instance, maybe because your application just processes one large document once, you will get best performance with large or huge pages. Under Linux, you can enable transparent huge pages with a command like echo always > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled (root access may be required). It may be more difficult to achieve the same result under other systems like macOS or Windows.
In general, when running benchmarks over large files, we recommend that you report performance numbers with and without huge pages if possible. Furthermore, you should amortize the parsing (e.g., by parsing several large files) to distinguish the time spent parsing from the time spent allocating memory.
Including simdjson
Code usage and example
The main API involves allocating a document::parser, and calling parser.parse() to create a fully navigable document-object-model (DOM) view of a JSON document. The DOM can be accessed via JSON Pointer paths, or as an iterator (document::iterator(doc)). See 'Navigating the parsed document' for more.
All examples below use use #include "simdjson.h", #include "simdjson.cpp" and using namespace simdjson;.
The simplest API to get started is document::parse(), which allocates a new parser, parses a string, and returns the DOM. This is less efficient if you're going to read multiple documents, but as long as you're only parsing a single document, this will do just fine.
auto [doc, error] = document::parse("[ 1, 2, 3 ]"_padded);
if (error) { cerr << "Error: " << error << endl; exit(1); }
cout << doc;
If you're using exceptions, it gets even simpler (simdjson won't use exceptions internally, so you'll only pay the performance cost of exceptions in your own calling code):
cout << document::parse("[ 1, 2, 3 ]"_padded);
If you're wondering why the examples above use _padded, it's because the simdjson library requires SIMDJSON_PADDING extra bytes at the end of a string (it doesn't matter if the bytes are initialized). _padded
is a way of creating a padded_string class, which assures us we have enough allocation.
padded_string json = "[ 1, 2, 3 ]"_padded;
cout << document::parse(json);
You can also load from a file with parser.load():
document::parser parser;
cout << parser.load(filename);
Reusing the parser for maximum efficiency
If you're using simdjson to parse multiple documents, or in a loop, you should make a parser once and reuse it. simdjson will allocate and retain internal buffers between parses, keeping buffers hot in cache and keeping allocation to a minimum.
document::parser parser;
for (padded_string json : { string("[1, 2, 3]"), string("true"), string("[ true, false ]") }) {
document& doc = parser.parse(json);
cout << doc;
}
If you are running a server loop and want to limit the document size to keep server memory constant, you can set a maximum capacity:
document::parser parser(1024*1024); // Set max capacity to 1MB
for (int i=0;i<argc;i++) {
auto [doc, error] = parser.parse(get_corpus(argv[i]));
if (error == CAPACITY) { cerr << "JSON files larger than 1MB are not supported!" << endl; exit(1); }
if (error) { cerr << error << endl; exit(1); }
cout << doc;
}
If you want absolutely constant memory usage, you can even allocate the capacity yourself at the beginning:
document::parser parser(0); // This parser is not allowed to auto-allocate
auto alloc_error = parser.set_capacity(1024*1024); // Set initial capacity to 1MB
if (alloc_error) { exit(1); };
for (int i=0;i<argc;i++) {
auto [doc, error] = parser.parse(get_corpus(argv[i]));
if (error == CAPACITY) { cerr << "JSON files larger than 1MB are not supported!" << endl; exit(1); }
if (error) { cerr << error << endl; exit(1); }
cout << doc;
}
Newline-Delimited JSON (ndjson) and JSON lines
The simdjson library also support multithreaded JSON streaming through a large file containing many smaller JSON documents in either ndjson or JSON lines format. If your JSON documents all contain arrays or objects, we even support direct file concatenation without whitespace. The concatenated file has no size restrictions (including larger than 4GB), though each individual document must be less than 4GB.
Here is a simple example, using single header simdjson:
#include "simdjson.h"
#include "simdjson.cpp"
int parse_file(const char *filename) {
simdjson::document::parser parser;
for (const document &doc : parser.load_many(filename)) {
// do something with the document ...
}
}
Usage: easy single-header version
See the singleheader directory for a single header version. See the included file "amalgamation_demo.cpp" for usage. This requires no specific build system: just copy the files in your project in your include path. You can then include them quite simply:
#include <iostream>
#include "simdjson.h"
#include "simdjson.cpp"
using namespace simdjson;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
document::parser parser;
auto [doc, error] = parser.load(argv[1]);
if(error) {
std::cout << "not valid: " << error << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "valid" << std::endl;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Note: In some settings, it might be desirable to precompile simdjson.cpp instead of including it.
Usage (old-school Makefile on platforms like Linux or macOS)
Requirements: recent clang or gcc, and make. We recommend at least GNU GCC/G++ 7 or LLVM clang 6. A 64-bit system like Linux or macOS is expected.
To test:
make
make test
To run benchmarks:
make parse
./parse jsonexamples/twitter.json
Under Linux, the parse command gives a detailed analysis of the performance counters.
To run comparative benchmarks (with other parsers):
make benchmark
Usage (CMake on 64-bit platforms like Linux or macOS)
Requirements: We require a recent version of cmake. On macOS, the easiest way to install cmake might be to use brew and then type
brew install cmake
There is an equivalent brew on Linux which works the same way as well.
You need a recent compiler like clang or gcc. We recommend at least GNU GCC/G++ 7 or LLVM clang 6. For example, you can install a recent compiler with brew:
brew install gcc@8
Optional: You need to tell cmake which compiler you wish to use by setting the CC and CXX variables. Under bash, you can do so with commands such as export CC=gcc-7 and export CXX=g++-7.
Building: While in the project repository, do the following:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
make test
CMake will build a library. By default, it builds a shared library (e.g., libsimdjson.so on Linux).
You can build a static library:
mkdir buildstatic
cd buildstatic
cmake -DSIMDJSON_BUILD_STATIC=ON ..
make
make test
In some cases, you may want to specify your compiler, especially if the default compiler on your system is too old. You may proceed as follows:
brew install gcc@8
mkdir build
cd build
export CXX=g++-8 CC=gcc-8
cmake ..
make
make test
Usage (CMake on 64-bit Windows using Visual Studio)
We assume you have a common 64-bit Windows PC with at least Visual Studio 2017 and an x64 processor with AVX2 support (2013 Intel Haswell or later) or SSE 4.2 + CLMUL (2010 Westmere or later).
- Grab the simdjson code from GitHub, e.g., by cloning it using GitHub Desktop.
- Install CMake. When you install it, make sure to ask that
cmakebe made available from the command line. Please choose a recent version of cmake. - Create a subdirectory within simdjson, such as
VisualStudio. - Using a shell, go to this newly created directory.
- Type
cmake -DCMAKE_GENERATOR_PLATFORM=x64 ..in the shell while in theVisualStudiorepository. (Alternatively, if you want to build a DLL, you may use the command linecmake -DCMAKE_GENERATOR_PLATFORM=x64 -DSIMDJSON_BUILD_STATIC=OFF ...) - This last command (
cmake ...) created a Visual Studio solution file in the newly created directory (e.g.,simdjson.sln). Open this file in Visual Studio. You should now be able to build the project and run the tests. For example, in theSolution Explorerwindow (available from theViewmenu), right-clickALL_BUILDand selectBuild. To test the code, still in theSolution Explorerwindow, selectRUN_TESTSand selectBuild.
Usage (Using vcpkg on 64-bit Windows, Linux and macOS)
vcpkg users on Windows, Linux and macOS can download and install simdjson with one single command from their favorite shell.
On 64-bit Linux and macOS:
$ ./vcpkg install simdjson
will build and install simdjson as a static library.
On Windows (64-bit):
.\vcpkg.exe install simdjson:x64-windows
will build and install simdjson as a shared library.
.\vcpkg.exe install simdjson:x64-windows-static
will build and install simdjson as a static library.
These commands will also print out instructions on how to use the library from MSBuild or CMake-based projects.
If you find the version of simdjson shipped with vcpkg is out-of-date, feel free to report it to vcpkg community either by submitting an issue or by creating a PR.
Tools
json2json mydoc.jsonparses the document, constructs a model and then dumps back the result to standard output.json2json -d mydoc.jsonparses the document, constructs a model and then dumps model (as a tape) to standard output. The tape format is described in the accompanying filetape.md.minify mydoc.jsonminifies the JSON document, outputting the result to standard output. Minifying means to remove the unneeded white space characters.jsonpointer mydoc.json <jsonpath> <jsonpath> ... <jsonpath>parses the document, constructs a model and then processes a series of JSON Pointer paths. The result is itself a JSON document.
Scope
We provide a fast parser, that fully validates an input according to various specifications. The parser builds a useful immutable (read-only) DOM (document-object model) which can be later accessed.
To simplify the engineering, we make some assumptions.
- We support UTF-8 (and thus ASCII), nothing else (no Latin, no UTF-16). We do not believe this is a genuine limitation, because we do not think there is any serious application that needs to process JSON data without an ASCII or UTF-8 encoding. If the UTF-8 contains a leading BOM, it should be omitted: the user is responsible for detecting and skipping the BOM; UTF-8 BOMs are discouraged.
- All strings in the JSON document may have up to 4294967295 bytes in UTF-8 (4GB). To enforce this constraint, we refuse to parse a document that contains more than 4294967295 bytes (4GB). This should accommodate most JSON documents.
- As allowed by the specification, we allow repeated keys within an object (other parsers like sajson do the same).
- The simdjson library is fast for JSON documents spanning a few bytes up to many megabytes.
We do not aim to provide a general-purpose JSON library. A library like RapidJSON offers much more than just parsing, it helps you generate JSON and offers various other convenient functions. We merely parse the document.
Features
- The input string is unmodified. (Parsers like sajson and RapidJSON use the input string as a buffer.)
- We parse integers and floating-point numbers as separate types which allows us to support large signed 64-bit integers in [-9223372036854775808,9223372036854775808), like a Java
longor a C/C++long longand large unsigned integers up to the value 18446744073709551615. Among the parsers that differentiate between integers and floating-point numbers, not all support 64-bit integers. (For example, sajson rejects JSON files with integers larger than or equal to 2147483648. RapidJSON will parse a file containing an overly long integer like 18446744073709551616 as a floating-point number.) When we cannot represent exactly an integer as a signed or unsigned 64-bit value, we reject the JSON document. - We support the full range of 64-bit floating-point numbers (binary64). The values range from
std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest()tostd::numeric_limits<double>::max(), so from -1.7976e308 all the way to 1.7975e308. Extreme values (less or equal to -1e308, greater or equal to 1e308) are rejected: we refuse to parse the input document. - We test for accurate float parsing with a perfect accuracy (ULP 0). Many parsers offer only approximate floating parsing. For example, RapidJSON also offers the option of accurate float parsing (
kParseFullPrecisionFlag) but it comes at a significant performance penalty compared to the default settings. By default, RapidJSON tolerates an error of 3 ULP. - We do full UTF-8 validation as part of the parsing. (Parsers like fastjson, gason and dropbox json11 do not do UTF-8 validation. The sajson parser does incomplete UTF-8 validation, accepting code point sequences like 0xb1 0x87.)
- We fully validate the numbers. (Parsers like gason and ultranjson will accept
[0e+]as valid JSON.) - We validate string content for unescaped characters. (Parsers like fastjson and ultrajson accept unescaped line breaks and tabs in strings.)
- We fully validate the white-space characters outside of the strings. Parsers like RapidJSON will accept JSON documents with null characters outside of strings.
Architecture
The parser works in two stages:
- Stage 1. (Find marks) Identifies quickly structure elements, strings, and so forth. We validate UTF-8 encoding at that stage.
- Stage 2. (Structure building) Involves constructing a "tree" of sort (materialized as a tape) to navigate through the data. Strings and numbers are parsed at this stage.
JSON Pointer
We can navigate the parsed JSON using JSON Pointers as per the RFC6901 standard.
You can build a tool (jsonpointer) to parse a JSON document and then issue an array of JSON Pointer queries:
make jsonpointer
./jsonpointer jsonexamples/small/demo.json /Image/Width /Image/Height /Image/IDs/2
./jsonpointer jsonexamples/twitter.json /statuses/0/id /statuses/1/id /statuses/2/id /statuses/3/id /statuses/4/id /statuses/5/id
In C++, given a document::parser, we can move to a node with the move_to method, passing a std::string representing the JSON Pointer query.
Navigating the parsed document
From a simdjson::document::parser instance, you can create an iterator (of type simdjson::document::parser::Iterator which is in fact simdjson::document::parser::BasicIterator<DEFAULT_MAX_DEPTH> ) via a constructor:
document::parser::Iterator pjh(parser); // parser is a ParsedJSON
You then have access to the following methods on the resulting simdjson::document::parser::Iterator instance:
bool is_ok() const: whether you have a valid iterator, will be false if your parent parsed document::parser is not a valid JSON.size_t get_depth() const: returns the current depth (start at 1 with 0 reserved for the fictitious root node)int8_t get_scope_type() const: a scope is a series of nodes at the same depth, typically it is either an object ({) or an array ([). The root node has type 'r'.bool move_forward(): move forward in document orderuint8_t get_type() const: retrieve the character code of what we're looking at:[{"slutfnare the possibilitiesint64_t get_integer() const: get the int64_t value at this node; valid only if get_type() is "l"uint64_t get_unsigned_integer() const: get the value as uint64; valid only if get_type() is "u"const char *get_string() const: get the string value at this node (NULL ended); valid only if get_type() is ", note that tabs, and line endings are escaped in the returned value, return value is valid UTF-8, it may contain NULL chars, get_string_length() determines the true string length.uint32_t get_string_length() const: return the length of the string in bytesdouble get_double() const: get the double value at this node; valid only if gettype() is "d"bool is_object_or_array() const: self-explanatorybool is_object() const: self-explanatorybool is_array() const: self-explanatorybool is_string() const: self-explanatorybool is_integer() const: self-explanatorybool is_unsigned_integer() const: Returns true if the current type of node is an unsigned integer. You can get its value withget_unsigned_integer(). Only a large value, which is out of range of a 64-bit signed integer, is represented internally as an unsigned node. On the other hand, a typical positive integer, such as 1, 42, or 1000000, is as a signed node. Be aware this function returns false for a signed node.bool is_double() const: self-explanatorybool is_number() const: self-explanatorybool is_true() const: self-explanatorybool is_false() const: self-explanatorybool is_null() const: self-explanatorybool is_number() const: self-explanatorybool move_to_key(const char *key): when at {, go one level deep, looking for a given key, if successful, we are left pointing at the value, if not, we are still pointing at the object ({) (in case of repeated keys, this only finds the first one). We seek the key using C's strcmp so if your JSON strings contain NULL chars, this would trigger a false positive: if you expect that to be the case, take extra precautions. Furthermore, we do the comparison character-by-character without taking into account Unicode equivalence.bool move_to_key_insensitive(const char *key): as above, but case insensitive lookupbool move_to_key(const char *key, uint32_t length): as above except that the target can contain NULL charactersvoid move_to_value(): when at a key location within an object, this moves to the accompanying, value (located next to it). This is equivalent but much faster than callingnext().bool move_to_index(uint32_t index): when at[, go one level deep, and advance to the given index, if successful, we are left pointing at the value,i f not, we are still pointing at the arraybool move_to(const char *pointer, uint32_t length): Moves the iterator to the value corresponding to the json pointer. Always search from the root of the document. If successful, we are left pointing at the value, if not, we are still pointing the same value we were pointing before the call. The json pointer follows the rfc6901 standard's syntax: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6901bool move_to(const std::string &pointer): same as above but with a std::string parameterbool next(): Within a given scope (series of nodes at the same depth within either an array or an object), we move forward. Thus, given [true, null, {"a":1}, [1,2]], we would visit true, null, { and [. At the object ({) or at the array ([), you can issue a "down" to visit their content. valid if we're not at the end of a scope (returns true).bool prev(): Within a given scope (series of nodes at the same depth within either an array or an object), we move backward.bool up(): moves back to either the containing array or object (type { or [) from within a contained scope.bool down(): moves us to start of that deeper scope if it not empty. Thus, given [true, null, {"a":1}, [1,2]], if we are at the { node, we would move to the "a" node.void to_start_scope(): move us to the start of our current scope, a scope is a series of nodes at the same levelvoid rewind(): repeatedly calls up until we are at the root of the documentbool print(std::ostream &os, bool escape_strings = true) const: print the node we are currently pointing at
Here is a code sample to dump back the parsed JSON to a string:
document::parser::Iterator pjh(parser);
if (!pjh.is_ok()) {
std::cerr << " Could not iterate parsed result. " << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
compute_dump(parser);
//
// where compute_dump is :
void compute_dump(document::parser::Iterator &pjh) {
if (pjh.is_object()) {
std::cout << "{";
if (pjh.down()) {
pjh.print(std::cout); // must be a string
std::cout << ":";
pjh.next();
compute_dump(pjh); // let us recurse
while (pjh.next()) {
std::cout << ",";
pjh.print(std::cout);
std::cout << ":";
pjh.next();
compute_dump(pjh); // let us recurse
}
pjh.up();
}
std::cout << "}";
} else if (pjh.is_array()) {
std::cout << "[";
if (pjh.down()) {
compute_dump(pjh); // let us recurse
while (pjh.next()) {
std::cout << ",";
compute_dump(pjh); // let us recurse
}
pjh.up();
}
std::cout << "]";
} else {
pjh.print(std::cout); // just print the lone value
}
}
The following function will find all user.id integers:
void simdjson_scan(std::vector<int64_t> &answer, document::parser::Iterator &i) {
while(i.move_forward()) {
if(i.get_scope_type() == '{') {
bool found_user = (i.get_string_length() == 4) && (memcmp(i.get_string(), "user", 4) == 0);
i.move_to_value();
if(found_user) {
if(i.is_object() && i.move_to_key("id",2)) {
if (i.is_integer()) {
answer.push_back(i.get_integer());
}
i.up();
}
}
}
}
}
In-depth comparisons
If you want to see how a wide range of parsers validate a given JSON file:
make allparserscheckfile
./allparserscheckfile myfile.json
For performance comparisons:
make parsingcompetition
./parsingcompetition myfile.json
For broader comparisons:
make allparsingcompetition
./allparsingcompetition myfile.json
Both the parsingcompetition and allparsingcompetition tools take a -t flag which produces
a table-oriented output that can be conveniently parsed by other tools.
Docker
One can run tests and benchmarks using docker. It especially makes sense under Linux. A privileged access may be needed to get performance counters.
git clone https://github.com/simdjson/simdjson.git
cd simdjson
docker build -t simdjson .
docker run --privileged -t simdjson
Other programming languages
We distinguish between "bindings" (which just wrap the C++ code) and a port to another programming language (which reimplements everything).
- ZippyJSON: Swift bindings for the simdjson project.
- pysimdjson: Python bindings for the simdjson project.
- simdjson-rs: Rust port.
- simdjson-rust: Rust wrapper (bindings).
- SimdJsonSharp: C# version for .NET Core (bindings and full port).
- simdjson_nodejs: Node.js bindings for the simdjson project.
- simdjson_php: PHP bindings for the simdjson project.
- simdjson_ruby: Ruby bindings for the simdjson project.
- simdjson-go: Go port using Golang assembly.
- rcppsimdjson: R bindings.
Various References
- Google double-conv
- How to implement atoi using SIMD?
- Parsing JSON is a Minefield 💣
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7159
- The Mison implementation in rust https://github.com/pikkr/pikkr
- http://rapidjson.org/md_doc_sax.html
- https://github.com/Geal/parser_benchmarks/tree/master/json
- Gron: A command line tool that makes JSON greppable https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=16727665
- GoogleGson https://github.com/google/gson
- Jackson https://github.com/FasterXML/jackson
- https://www.yelp.com/dataset_challenge
- RapidJSON. http://rapidjson.org/
Inspiring links:
- https://auth0.com/blog/beating-json-performance-with-protobuf/
- https://gist.github.com/shijuvar/25ad7de9505232c87034b8359543404a
- https://github.com/frankmcsherry/blog/blob/master/posts/2018-02-11.md
Validating UTF-8 takes no more than 0.7 cycles per byte:
- https://github.com/lemire/fastvalidate-utf-8 https://lemire.me/blog/2018/05/16/validating-utf-8-strings-using-as-little-as-0-7-cycles-per-byte/
Remarks on JSON parsing
- The JSON spec defines what a JSON parser is:
A JSON parser transforms a JSON text into another representation. A JSON parser MUST accept all texts that conform to the JSON grammar. A JSON parser MAY accept non-JSON forms or extensions. An implementation may set limits on the size of texts that it accepts. An implementation may set limits on the maximum depth of nesting. An implementation may set limits on the range and precision of numbers. An implementation may set limits on the length and character contents of strings.
-
JSON is not JavaScript:
All JSON is Javascript but NOT all Javascript is JSON. So {property:1} is invalid because property does not have double quotes around it. {'property':1} is also invalid, because it's single quoted while the only thing that can placate the JSON specification is double quoting. JSON is even fussy enough that {"property":.1} is invalid too, because you should have of course written {"property":0.1}. Also, don't even think about having comments or semicolons, you guessed it: they're invalid. (credit:https://github.com/elzr/vim-json)
-
The structural characters are:
begin-array = [ left square bracket begin-object = { left curly bracket end-array = ] right square bracket end-object = } right curly bracket name-separator = : colon value-separator = , comma
Pseudo-structural elements
A character is pseudo-structural if and only if:
- Not enclosed in quotes, AND
- Is a non-whitespace character, AND
- Its preceding character is either: (a) a structural character, OR (b) whitespace.
This helps as we redefine some new characters as pseudo-structural such as the characters 1, G, n in the following:
{ "foo" : 1.5, "bar" : 1.5 GEOFF_IS_A_DUMMY bla bla , "baz", null }
Academic References
- T.Mühlbauer, W.Rödiger, R.Seilbeck, A.Reiser, A.Kemper, and T.Neumann. Instant loading for main memory databases. PVLDB, 6(14):1702–1713, 2013. (SIMD-based CSV parsing)
- Mytkowicz, Todd, Madanlal Musuvathi, and Wolfram Schulte. "Data-parallel finite-state machines." ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News. Vol. 42. No. 1. ACM, 2014.
- Lu, Yifan, et al. "Tree structured data processing on GPUs." Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering-Confluence, 2017 7th International Conference on. IEEE, 2017.
- Sidhu, Reetinder. "High throughput, tree automata based XML processing using FPGAs." Field-Programmable Technology (FPT), 2013 International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
- Dai, Zefu, Nick Ni, and Jianwen Zhu. "A 1 cycle-per-byte XML parsing accelerator." Proceedings of the 18th annual ACM/SIGDA international symposium on Field programmable gate arrays. ACM, 2010.
- Lin, Dan, et al. "Parabix: Boosting the efficiency of text processing on commodity processors." High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), 2012 IEEE 18th International Symposium on. IEEE, 2012. http://parabix.costar.sfu.ca/export/1783/docs/HPCA2012/final_ieee/final.pdf
- Deshmukh, V. M., and G. R. Bamnote. "An empirical evaluation of optimization parameters in XML parsing for performance enhancement." Computer, Communication and Control (IC4), 2015 International Conference on. IEEE, 2015.
- Moussalli, Roger, et al. "Efficient XML Path Filtering Using GPUs." ADMS@ VLDB. 2011.
- Jianliang, Ma, et al. "Parallel speculative dom-based XML parser." High Performance Computing and Communication & 2012 IEEE 9th International Conference on Embedded Software and Systems (HPCC-ICESS), 2012 IEEE 14th International Conference on. IEEE, 2012.
- Li, Y., Katsipoulakis, N.R., Chandramouli, B., Goldstein, J. and Kossmann, D., 2017. Mison: a fast JSON parser for data analytics. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 10(10), pp.1118-1129. http://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol10/p1118-li.pdf
- Cameron, Robert D., et al. "Parallel scanning with bitstream addition: An xml case study." European Conference on Parallel Processing. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011.
- Cameron, Robert D., Kenneth S. Herdy, and Dan Lin. "High performance XML parsing using parallel bit stream technology." Proceedings of the 2008 conference of the center for advanced studies on collaborative research: meeting of minds. ACM, 2008.
- Shah, Bhavik, et al. "A data parallel algorithm for XML DOM parsing." International XML Database Symposium. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009.
- Cameron, Robert D., and Dan Lin. "Architectural support for SWAR text processing with parallel bit streams: the inductive doubling principle." ACM Sigplan Notices. Vol. 44. No. 3. ACM, 2009.
- Amagasa, Toshiyuki, Mana Seino, and Hiroyuki Kitagawa. "Energy-Efficient XML Stream Processing through Element-Skipping Parsing." Database and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA), 2013 24th International Workshop on. IEEE, 2013.
- Medforth, Nigel Woodland. "icXML: Accelerating Xerces-C 3.1. 1 using the Parabix Framework." (2013).
- Zhang, Qiang Scott. Embedding Parallel Bit Stream Technology Into Expat. Diss. Simon Fraser University, 2010.
- Cameron, Robert D., et al. "Fast Regular Expression Matching with Bit-parallel Data Streams."
- Lin, Dan. Bits filter: a high-performance multiple string pattern matching algorithm for malware detection. Diss. School of Computing Science-Simon Fraser University, 2010.
- Yang, Shiyang. Validation of XML Document Based on Parallel Bit Stream Technology. Diss. Applied Sciences: School of Computing Science, 2013.
- N. Nakasato, "Implementation of a parallel tree method on a GPU", Journal of Computational Science, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 132-141, 2012.
Funding
The work is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada under grant number RGPIN-2017-03910.