Liteos_a FATFS需要提供格式化时设置卷标的功能,该功能在当前系统中缺失。 现在恢复该功能,使用方法与原来一致。即使用set_label设置卷标文本后,调用format对设备格式化。 Close #I3Y5G8 Signed-off-by: Far <yesiyuan2@huawei.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .gitee | ||
| apps | ||
| arch | ||
| bsd | ||
| compat/posix | ||
| drivers | ||
| figures | ||
| fs | ||
| kernel | ||
| lib | ||
| net | ||
| platform | ||
| security | ||
| shell | ||
| syscall | ||
| testsuites | ||
| tools | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| BUILD.gn | ||
| Kconfig | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| README_zh-HK.md | ||
| README_zh.md | ||
| TODOList.md | ||
| build.sh | ||
| config.mk | ||
| kernel_test.sources | ||
README.md
LiteOS Cortex-A
Introduction
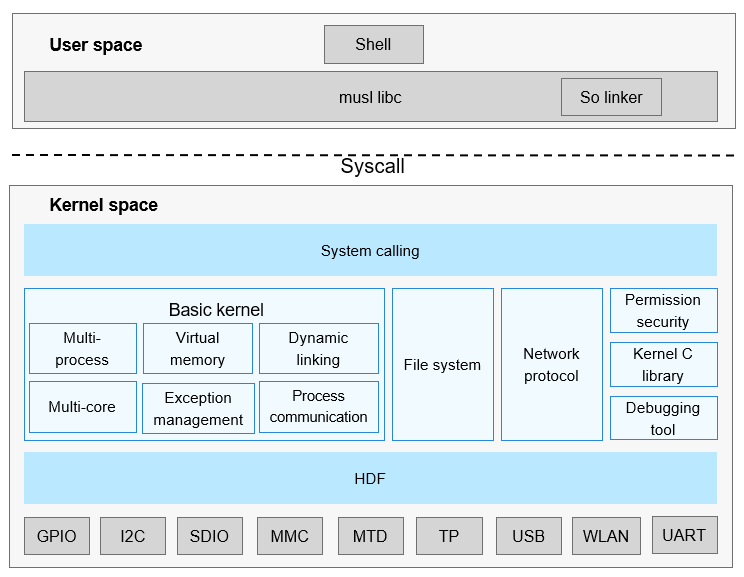
The OpenHarmony LiteOS Cortex-A is a new-generation kernel developed based on the Huawei LiteOS kernel. Huawei LiteOS is a lightweight operating system OS built for the Internet of Things IoT field. With the rapid development of the IoT industry, OpenHarmony LiteOS Cortex-A brings small-sized, low-power, and high-performance experience and builds a unified and open ecosystem for developers. In addition, it provides rich kernel mechanisms, more comprehensive Portable Operating System Interface POSIX, and a unified driver framework, Hardware Driver Foundation HDF, which offers unified access for device developers and friendly development experience for application developers. Figure 1 shows the architecture of the OpenHarmony LiteOS Cortex-A kernel.
Figure 1 Architecture of the OpenHarmony LiteOS Cortex-A kernel
Directory Structure
/kernel/liteos_a
├── apps # User-space init and shell application programs
├── arch # System architecture, such as ARM
│ └── arm # Code for ARM architecture
├── bsd # Code of the driver and adaptation layer module related to the FreeBSD, such as the USB module
├── compat # Kernel API compatibility
│ └── posix # POSIX APIs
├── drivers # Kernel drivers
│ └── char # Character device
│ ├── mem # Driver for accessing physical input/output (I/O) devices
│ ├── quickstart # APIs for quick start of the system
│ ├── random # Driver for random number generators
│ └── video # Framework of the framebuffer driver
├── fs # File system module, which mainly derives from the NuttX open-source project
│ ├── fat # FAT file system
│ ├── jffs2 # JFFS2 file system
│ ├── include # Header files exposed externally
│ ├── nfs # NFS file system
│ ├── proc # proc file system
│ ├── ramfs # RAMFS file system
│ └── vfs # VFS layer
├── kernel # Kernel modules including the process, memory, and IPC modules
│ ├── base # Basic kernel modules including the scheduling and memory modules
│ ├── common # Common components used by the kernel
│ ├── extended # Extended kernel modules including the dynamic loading, vDSO, and LiteIPC modules
│ ├── include # Header files exposed externally
│ └── user # Init process loading
├── lib # Kernel library
├── net # Network module, which mainly derives from the lwIP open-source project
├── platform # Code for supporting different systems on a chip (SOCs), such as Hi3516D V300
│ ├── hw # Logic code related to clocks and interrupts
│ ├── include # Header files exposed externally
│ └── uart # Logic code related to the serial port
├── platform # Code for supporting different systems on a chip (SOCs), such as Hi3516D V300
├── security # Code related to security features, including process permission management and virtual ID mapping management
├── syscall # System calling
└── tools # Building tools as well as related configuration and code
Constraints
- Programming languages: C and C++
- Applicable development boards: Hi3518E V300 and Hi3516D V300
- Hi3518E V300 uses the JFFS2 file system by default, and Hi3516D V300 uses the FAT file system by default.
Usage
OpenHarmony LiteOS Cortex-A supports the Hi3518E V300 and Hi3516D V300. You can develop and run your applications based on both development boards.
Preparations
You need to set up the compilation environment on Linux.
- For Hi3518E V300, see Setting Up the Hi3518 Development Environment.
- For Hi3516D V300, see Setting Up the Hi3516 Development Environment.
Source Code Acquisition
Download and decompress a set of source code on a Linux server to acquire the source code. For more acquisition methods, see Source Code Acquisition.
Compilation and Building
For details about how to develop the first application, see:
Repositories Involved
kernel_liteos_a